|
MAYO LAKE MINERALS - YUKON PROPERTIES
SYNOPSIS PROPERTIES FLAGSHIP Carlin-Roop EARLY-MID STAGE Anderson-Davidson Trail-Minto BLUE SKY Edmonton Cascade GEOLOGIC OVERVIEW Yukon Mayo Lake Area Geology Mayo Lake Area Mineralization REPORTS November 17, 2021 Carlin-Roop NI 43-101 Technical Report Carlin-Roop Silver Project, Mayo Lake District, Yukon Territory, Canada |
CASCADE CLAIM GROUP
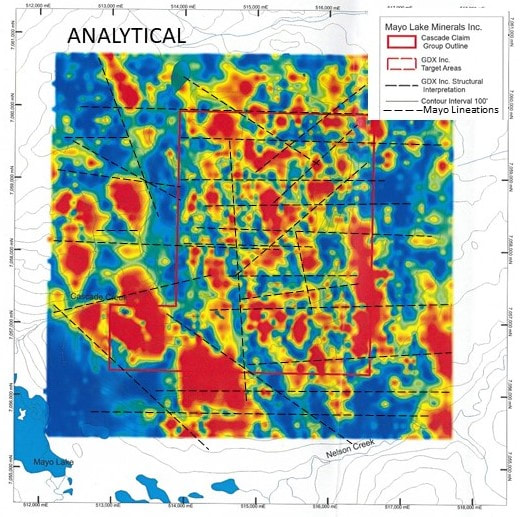
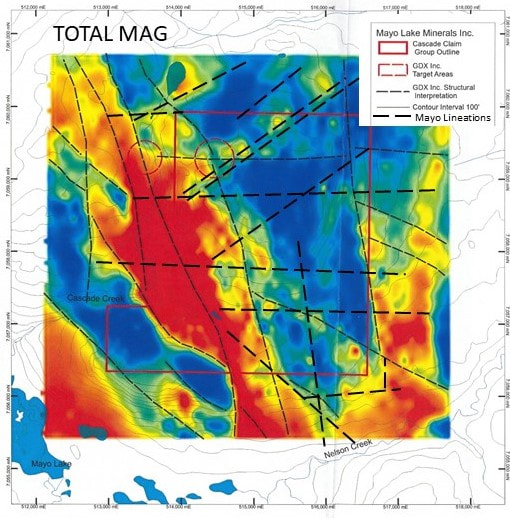
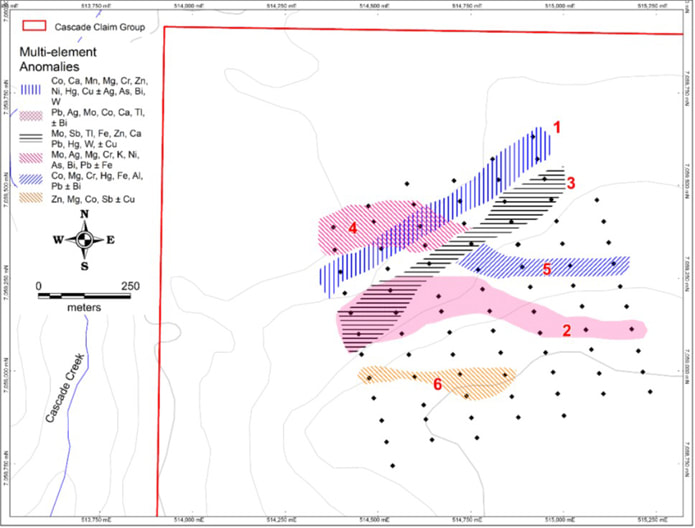
The Cascade claim group is composed of 40 contiguous quartz claims covering an area of 9.5 square kilometres near Mayo Lake. Cascade covers a moderately sloping prominence overlooking a former producing placer creek draining into the Nelson Arm of Mayo Lake. The claim group is also accessible from Mayo Lake, which has a boat launch at its west end. An old road leading from the lake crosses the south part of Cascade. The property is underlain by the Robert Service Thrust (RST), which is sub-horizontal. It includes a complex intermingling of Hyland Group Metasediments intruded by competent gabbroic rocks and amphibolite dykes. Rock was also intensely strained during the subsequent Tombstone thrusting. The surface cover is a mixture of colluvium and till. Cascade has been subjected to multiple glaciations. The ice was probably cold-based due to the elevation of the upland, and transport of rock and debris was minimal. The geophysics also indicates numerous lineations (Figure 26) suggestive of jointing and faulting both characteristic of complexe multi-layered thrust traces. Geophysics flown in 2012 by MLM suggests that the surface trace of the RST is folded around the nose of the Mayo Lake Antiform on or adjacent to the property. This structurally complex zone has good potential to host mineralized structures. Reconnaissance sampling suggested the presence of a gold in soil anomaly, with the most anomalous sample yielding 2.25 g Au/t. Definition sampling in 2017 has delineated five gold in soil anomalies (Figure 27). The anomalies are all open in at least one direction. Two anomalies have associated element anomalies suggesting a felsic intrusive or skarn-type provenance. The other Au anomalies have element associations suggesting intrusion related or orogenic-type provenances for the gold; two of them have strong As and Sb associations. In 2018, MLM reanalyzed soil samples for Au by fire assay to confirm previous Au in soil anomalies defined by INAA and ICP-MS after acid digestion techniques because of the possibility that gold values may have been negated or muted where graphite was present in the soil. The results did not indicate any obvious affects from the graphite or any other soil component. Further definition sampling around the exterior of the original soils grid extended those anomalies along the east part of the grid. A new grid in the south part of the property delineated one E-W trending gold in soil anomaly (Figure 10). In the future, more detailed soil sampling is warranted to define potential gold mineralization in areas where reconnaissance soil sampling and airborne magnetics indicate good potential for gold mineralization, mainly to the east and north of the northern grid. |
|
MAILING ADDRESS
Mayo Lake Minerals Box 158, Carp On K0A 1L0 |
|